Benefits Of Keto
In recent years, many scientific studies showcase the vast contribution of a keto diet to our overall wellness and when addressing metabolic syndrome1, which is closely linked to obesity and insulin resistance. It is vital that you have a clear picture of these benefits, what keto is best used for and how.
Reversal Of Diabetes And Prediabetes
When most carbs and sugars are eliminated, it is no surprise why the keto diet works well for people with diabetes to control their blood sugar and insulin levels. Many will notice an immediate drop in their blood sugar after starting a keto diet for just a few days. Some studies showed that a long-term keto diet2, where patients are in nutritional ketosis, can sustainably reverse type 2 diabetes due to improved insulin sensitivity3, fasting blood glucose level4 and reduction in inflammation. When blood sugar is no longer chronically elevated and is more stabilized, patients can make medication adjustments with professional medical supervision and advice.
Weight Loss And Appetite Regulation
The most commonly cited health benefits of the keto diet are weight loss5, mainly because of the highly restrictive carb intake and, at the same time, converting people to a fat-heavy and fat-burning diet. Fewer carbs also mean no drastic fluctuations in blood sugar4 to stimulate sugar crashes, cravings and hunger. Your hormones such as insulin, ghrelin and leptin are in balance6, and you feel satiated

Cardiovascular Health
For a long time, fat has been deemed the culprit of heart diseases. However, new evidence7 from research addressing this controversy found no link between total dietary fat or saturated fat and heart disease for most people. Patients who are carriers of the ApoE3/4 genes and/or with hypercholesterolemia must be cautious and get proper medical advice if they want to increase dietary fats as a therapeutic intervention. Diets low in carbs and higher in fats8 have significantly improved the biomarkers9 associated with cardiovascular health in various studies. When following a keto diet, body fat, insulin, and blood sugar levels generally improve, contributing to lower blood pressure, triglycerides concentration, LDL cholesterol and higher HDL cholesterol10. Aside from reducing the LDL cholesterol levels, recent studies also showed that the average particle size of LDL cholesterol increases, while the small dense particles associated with vascular damage, heart disease11 or stroke drastically decrease.
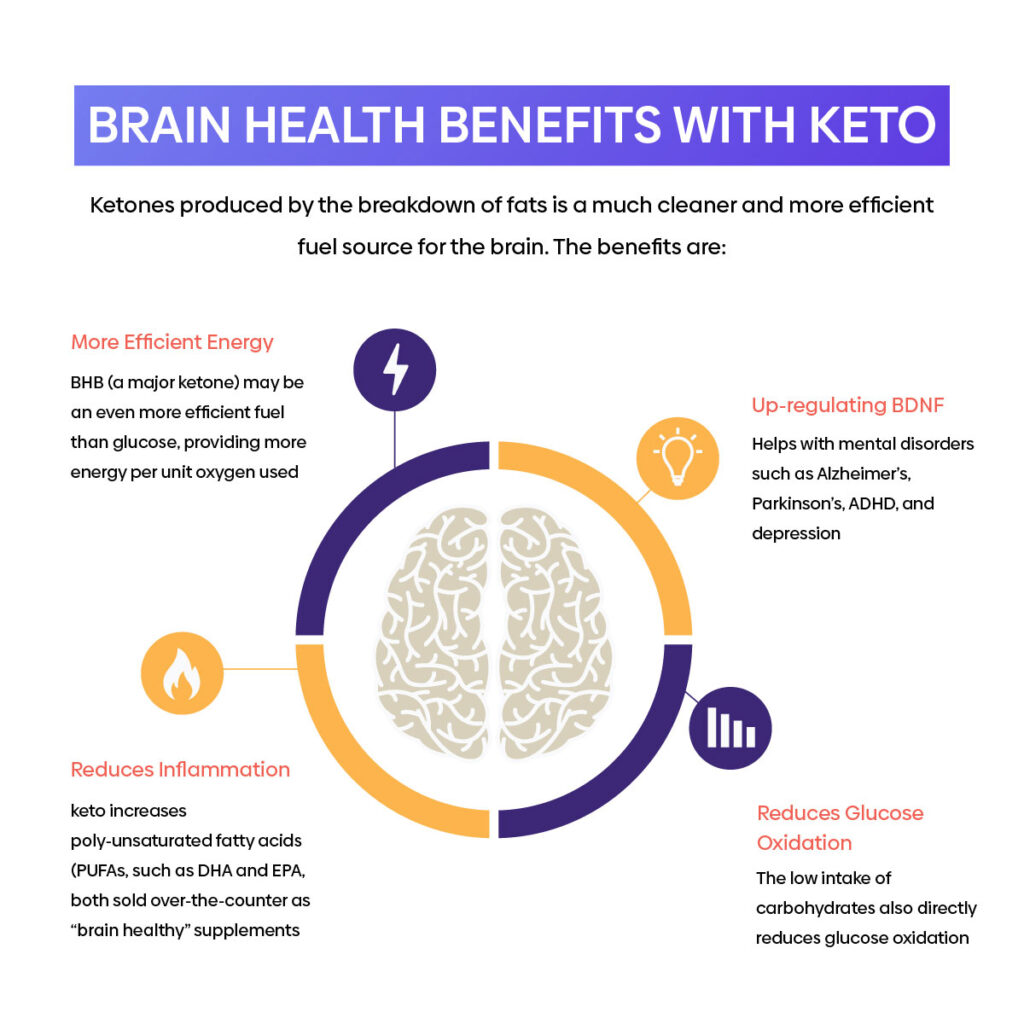
Brain Health
One of the first benefits you will likely notice when following the keto diet is improved mental performance and clarity. This is because the ketones produced by the breakdown of fats is a much cleaner and more efficient fuel source for the brain. This diet was initially used as a therapeutic treatment to treat neurological conditions, in particular epileptic seizures12. Research has also shown that ketones can improve neurodegenerative disorders by up-regulating BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor). BDNF is responsible for regulating the growth of neural connections in the brain. Low BDNF have been correlated with mental disorders such as Alzheimer’s13, Parkinson’s, ADHD, and depression14.
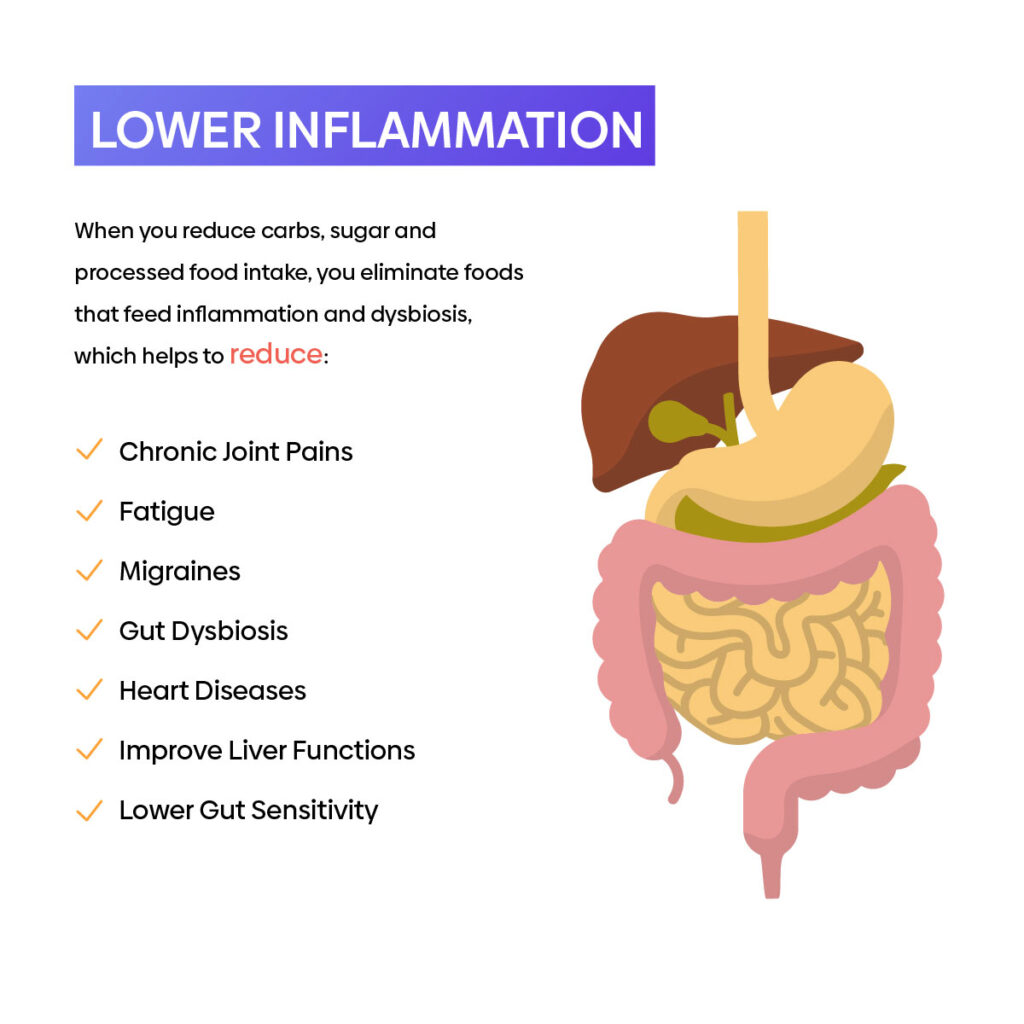
Inflammation And Gut Health
Chronic inflammation is one of the main contributing factors to many health conditions, including chronic joint pains, fatigue, migraines, gut dysbiosis15, heart diseases, to name a few. A clean keto diet is naturally an anti-inflammatory13 diet. When you reduce carbs, sugar and processed food intake, you eliminate foods that feed inflammation and dysbiosis. At the same time, you are introducing a host of anti-inflammatory foods into your diet, including eggs, olive oil, fatty fish, leafy greens and non-starchy vegetables, avocados, some fermented foods, all of which also contribute to your gut health1. When in ketosis, a type of ketone, BHB (ß-hydroxybutyrate), is released, a robust anti-inflammatory chemical that inhibits inflammatory pathways in the body.
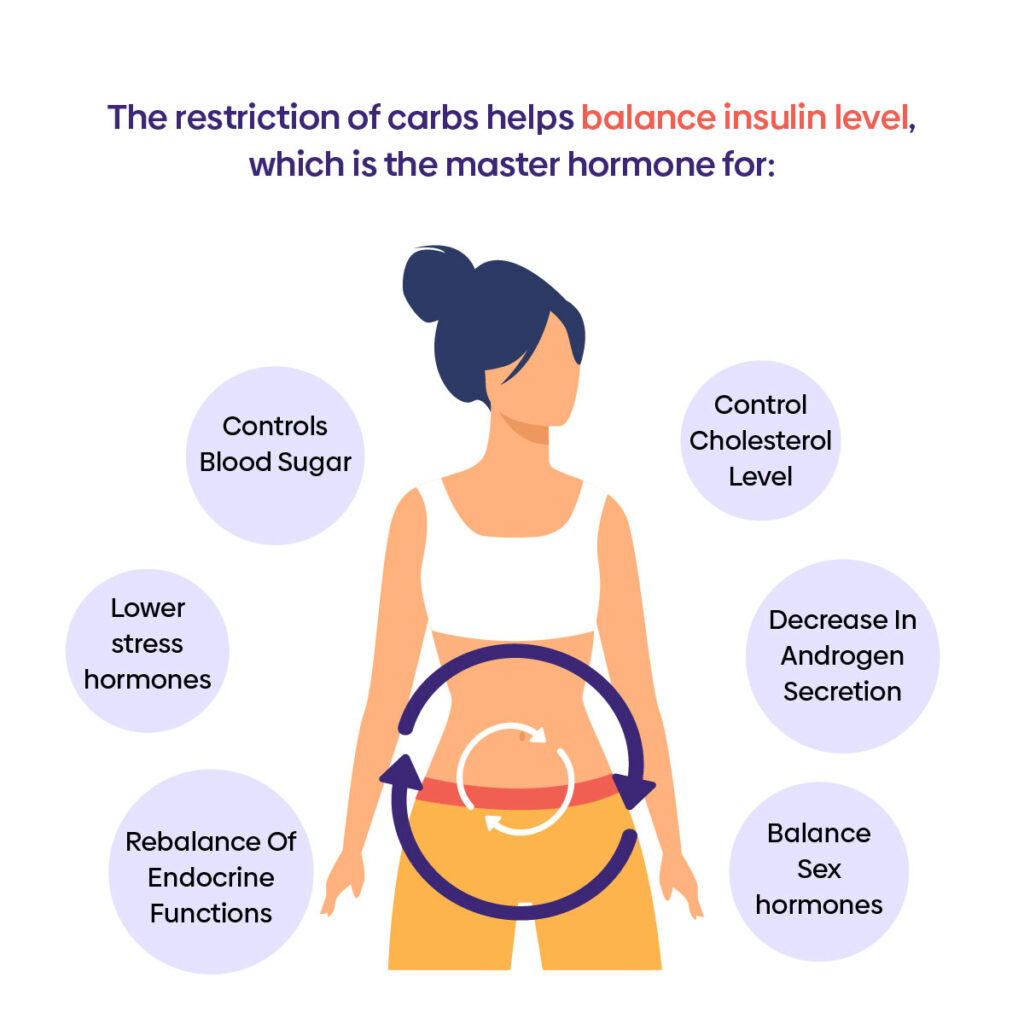
Hormonal Health
The increase of healthy fat consumption has been shown to support healthy hormone production and maintenance of the endocrine system16. The restriction of carbs helps balance insulin level, the master hormone that controls blood sugar, cholesterol, sex hormones, stress hormones and much more. For example, Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is associated with obesity, insulin resistance and overproduction of androgen hormones, which all can be improved by following a keto diet. There is evidence that this high-fat diet also leads to a decrease in androgen secretion and the rebalance of endocrine functions.
More About Keto
References
See the list- Cucuzzella, M. T., Tondt, J., Dockter, N. E., Saslow, L., & Wood, T. R. (2017). A low-carbohydrate survey: Evidence for sustainable metabolic syndrome reversal. Journal of Insulin Resistance, 2(1), 25. https://insulinresistance.org/index.php/jir/article/view/30/88
- Dashti HM; Mathew TC; Khadada M; Al-Mousawi M; Talib H; Asfar SK; Behbahani AI; Al-Zaid NS; (2007, April 20). Beneficial effects of ketogenic diet in obese diabetic subjects. Molecular and cellular biochemistry. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17447017/
- Veech, R. L. (2004). The therapeutic implications of ketone bodies: The effects of ketone bodies in pathological conditions: ketosis, ketogenic diet, redox states, insulin resistance, and mitochondrial metabolism. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes, and Essential Fatty Acids, 70(3), 309–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plefa.2003.09.007
- Westman, E. C., Yancy, W. S., Mavropoulos, J. C., Marquart, M., & McDuffie, J. R. (2008). The effect of a low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet versus a low-glycemic index diet on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutrition & Metabolism, 5, 36. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-7075-5-36
- Ketogenic diet: Is it good for diabetes and weight loss? (n.d.). EndocrineWeb. Retrieved September 9, 2021, from https://www.endocrineweb.com/news/diabetes/59538-ketogenic-diet-is-it-good-for-diabetes-and-weight-loss
- Sumithran, P., Prendergast, L. A., Delbridge, E., Purcell, K., Shulkes, A., Kriketos, A., & Proietto, J. (2013). Ketosis and appetite-mediating nutrients and hormones after weight loss. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 67(7), 759–764. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2013.90
- Siri-Tarino PW, Chiu S, Bergeron N, Krauss RM. Saturated fats versus polyunsaturated fats versus carbohydrates for cardiovascular disease prevention and treatment. Annu Rev Nutr. 2015 Jul 17, 35:517-43.
- Estruch R, Ros E, Salas-Salvado J, et al.; PR EDIMED Study Investigators. Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease with a Mediterranean diet. N Engl J Med. 2013 Apr. 4; 386(14): 1279-90.
- Sharman, M. J., Kraemer, W. J., Love, D. M., Avery, N. G., Gómez, A. L., Scheett, T. P., & Volek, J. S. (2002). A ketogenic diet favorably affects serum biomarkers for cardiovascular disease in normal-weight men. The Journal of Nutrition, 132(7), 1879–1885. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/132.7.1879
- Bennet, A. M., Di Angelantonio, E., Ye, Z., Wensley, F., Dahlin, A., Ahlbom, A., Keavney, B., Collins, R., Wiman, B., de Faire, U., & Danesh, J. (2007). Association of apolipoprotein E genotypes with lipid levels and coronary risk. JAMA, 298(11), 1300–1311. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.298.11.1300
- Kosinski, C., & Jornayvaz, F. R. (2017). Effects of ketogenic diets on cardiovascular risk factors: Evidence from animal and human studies. Nutrients, 9(5), 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9050517
- Masino, S. A., & Rho, J. M. (2012). Mechanisms of ketogenic diet action. In J. L. Noebels, M. Avoli, M. A. Rogawski, R. W. Olsen, & A. V. Delgado-Escueta (Eds.), Jasper’s Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies (4th ed.). National Center for Biotechnology Information (US). http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK98219/
- Pinto, A., Bonucci, A., Maggi, E., Corsi, M., & Businaro, R. (2018). Anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of ketogenic diet: New perspectives for neuroprotection in alzheimer’s disease. Antioxidants, 7(5), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7050063
- Low carb and mental health: The food-mood connection. (n.d.). Diet Doctor. Retrieved September 9, 2021, from https://www.dietdoctor.com/low-carb/mental-health-guides
- Austin, G. L., Dalton, C. B., Hu, Y., Morris, C. B., Hankins, J., Weinland, S. R., Westman, E. C., Yancy, W. S., & Drossman, D. A. (2009). A very low-carbohydrate diet improves symptoms and quality of life in diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology : The Official Clinical Practice Journal of the American Gastroenterological Association, 7(6), 706-708.e1. https://www.cghjournal.org/article/S1542-3565(09)00198-0/fulltext
- Gupta, L., Khandelwal, D., Kalra, S., Gupta, P., Dutta, D., & Aggarwal, S. (2017). Ketogenic diet in endocrine disorders: Current perspectives. Journal of Postgraduate Medicine, 63(4), 242–251. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5664869/